The use of Coated Aluminum Coil across modern ACP Line (Aluminum Composite Panel production line) applications has expanded significantly as industries pursue materials that balance strength, formability, and visual appeal. In manufacturing and construction, the performance of coated aluminum depends heavily on its surface treatment. This process not only influences appearance but also determines how well the coil resists corrosion, weathering, and mechanical stress over time. Understanding how surface coating affects durability helps users select the right specifications for various project requirements.
The Role of Surface Treatment in Aluminum Coil Production
Surface treatment serves as the foundation for long-term performance. Before coating, the aluminum coil typically undergoes several preparatory steps such as degreasing, chemical cleaning, and conversion coating. Each of these stages removes impurities and prepares the surface for uniform paint adhesion.
Conversion coatings—such as chromate or chrome-free alternatives—create a thin, corrosion-resistant layer that enhances bonding between the aluminum substrate and the subsequent paint or film. On an ACP Line, this preparation step is crucial because the aluminum sheets are later bonded to polymer cores. A well-treated surface ensures consistent adhesion, reducing delamination risks and maintaining panel stability in varying environmental conditions.
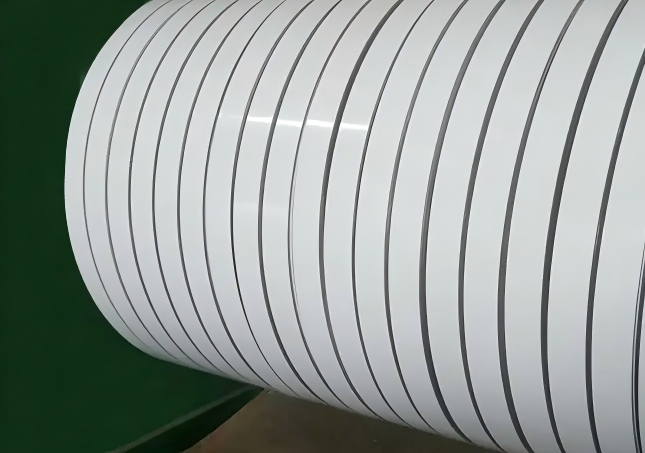

Types of Coating Systems and Their Functional Impact
Several coating systems are commonly applied to aluminum coils, each offering distinct protective and aesthetic qualities. Polyester, PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride), and polyurethane coatings are among the widely used in architectural and industrial settings.
Polyester coatings provide flexibility and good color retention for indoor or moderate outdoor use.
PVDF coatings offer resistance to ultraviolet radiation and chemical degradation, making them suitable for exterior facades exposed to harsh climates.
Polyurethane coatings deliver a balance of hardness and elasticity, ideal for applications that experience moderate mechanical stress.
The coating thickness, curing temperature, and application uniformity also contribute to overall performance. For instance, a uniform coating layer applied through a continuous ACP Line ensures that the surface remains evenly protected from oxidation, which can otherwise compromise both appearance and mechanical properties.
Environmental and Mechanical Factors Influencing Durability
Even with advanced coatings, real-world conditions play a decisive role in determining how long the aluminum coil will last. Temperature variations, humidity, ultraviolet exposure, and air pollutants all contribute to gradual wear. In coastal or industrial regions, salt and acidic gases can accelerate corrosion.
The durability of coated aluminum can be evaluated by its ability to maintain adhesion, gloss, and color stability after prolonged environmental exposure. Laboratory tests such as salt spray resistance, humidity chamber testing, and accelerated weathering simulations are often used to predict real-world performance. Manufacturers optimize the coating formula and process parameters based on these evaluations to ensure consistent quality across production batches.
Enhancing Adhesion and Corrosion Resistance on ACP Lines
On an ACP Line, adhesion between the aluminum coil and the core material determines the structural integrity of the final composite panel. The surface energy of the aluminum sheet must be properly controlled to ensure the bonding layer forms a stable interface. Treatments like corona discharge or plasma activation may be applied before lamination to improve bonding.
Moreover, the coating system must resist degradation during the lamination process, where heat and pressure are applied. The thermal stability of the coating prevents blistering or delamination, which could otherwise cause panel failure during installation or long-term use. Careful alignment between coating technology and ACP production parameters enhances not only visual quality but also structural reliability.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Even when high-quality coated aluminum is used, routine inspection and maintenance extend service life. Periodic cleaning removes pollutants and organic residues that may gradually attack the coating surface. Neutral pH detergents and soft cleaning tools are generally recommended to avoid damaging the protective layer.
Re-coating or touch-up procedures can also be applied if minor scratches or fading occur. In architectural applications, maintaining surface integrity helps preserve the overall appearance of building facades while preventing corrosion from spreading underneath damaged areas.
Practical Insights for Selection and Application
Selecting the right coated aluminum coil involves balancing environmental exposure, design goals, and cost considerations. For interior decorative panels, polyester-coated aluminum may be sufficient. However, for outdoor façades or transportation components exposed to severe conditions, PVDF-coated variants offer better long-term value.
When integrated into an ACP Line, matching the coating type to lamination temperature and bonding materials ensures consistent performance. Project planners and engineers can optimize outcomes by consulting material specifications and verifying compatibility between coating systems, adhesives, and substrate thickness.
In essence, the surface treatment of coated aluminum coil is more than a finishing step—it defines how well the material performs throughout its service life. Proper pretreatment, coating selection, and process control enable manufacturers and users alike to achieve both durability and aesthetic consistency, making the material a practical choice for a wide range of structural and decorative applications.

 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Português
Português русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى