The construction industry has been moving toward sustainable practices, and materials play a significant role in this transformation. Aluminum veneer panel has emerged as a practical solution for projects that aim to reduce environmental impact while maintaining design flexibility. Its lightweight structure, durability, and recyclability make it an appealing option for both commercial and residential buildings.

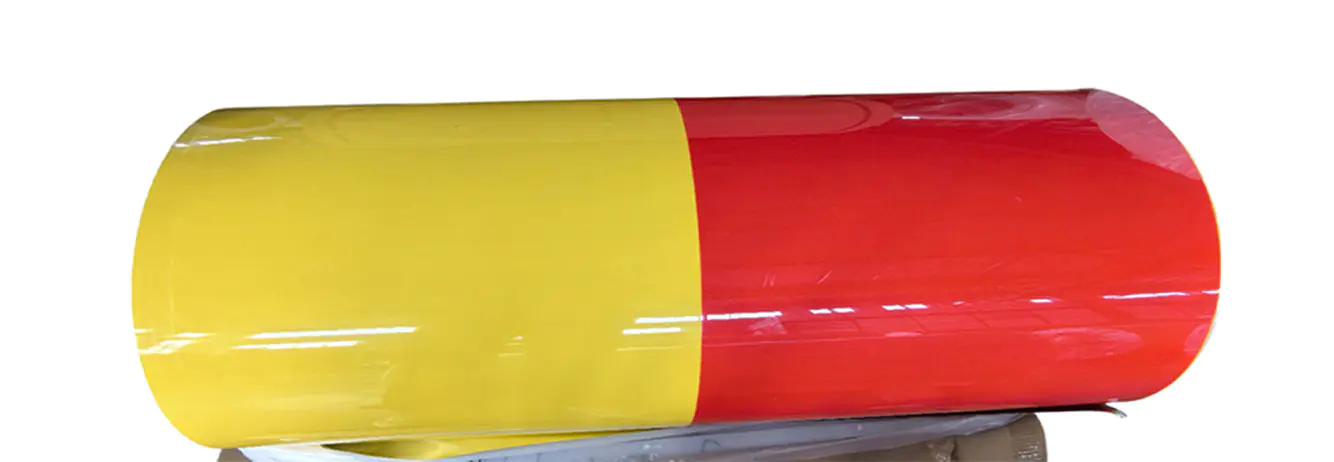
One notable advantage of aluminum veneer panel is its adaptability in modern architecture. Architects can shape it into various forms without compromising structural integrity. When paired with Color Coated Aluminum Coil, the panels gain additional protection against weathering and corrosion, extending the lifespan of the building facade. The combination allows for creative finishes, from subtle metallic sheens to vibrant colored surfaces, making it easier to align functional needs with aesthetic aspirations.
Sustainability goes beyond visual appeal. Aluminum veneer panel is entirely recyclable, which reduces waste and supports circular construction practices. Many construction projects now emphasize material reuse, and these panels can be repurposed or melted down without losing quality. Similarly, Color Coated Aluminum Coil is engineered to less the environmental footprint of production, using coatings that reduce energy consumption during manufacturing. Together, they contribute to a building process that is mindful of resource efficiency.
The installation process of aluminum veneer panel is another aspect that complements sustainable construction. Panels are lightweight yet sturdy, which simplifies handling and reduces the need for heavy machinery. This lowers energy consumption during assembly and shortens project timelines. In addition, when integrated with Color Coated Aluminum Coil, the panels maintain consistent quality and surface appearance, ensuring that maintenance is less frequent and easier to manage over time.
Thermal performance is increasingly important in sustainable design, and aluminum veneer panel can improve energy efficiency when combined with suitable insulation. Color Coated Aluminum Coil enhances the reflective properties of the panels, helping to manage solar heat gain. Buildings incorporating these materials often experience reduced heating and cooling demands, which translates into lower operational energy usage. Over the lifespan of a structure, these efficiency gains can advance to measurable reductions in environmental impact.
Designers also appreciate the versatility that aluminum veneer panel provides. Panels can be perforated, embossed, or coated in patterns that complement a building’s overall aesthetic. Color Coated Aluminum Coil expands these possibilities, offering a broad range of color and finish options without sacrificing durability. This flexibility allows designers to balance creativity with functional requirements, resulting in structures that are visually appealing and environmentally responsible.
Beyond individual buildings, the adoption of aluminum veneer panel in urban development contributes to larger-scale sustainability initiatives. The material’s long life, recyclability, and energy performance make it suitable for mixed-use projects, office complexes, and public infrastructure. Color Coated Aluminum Coil supports this trend by providing consistent quality and color retention, reducing the need for frequent replacements or refurbishments. Such attributes align with the growing emphasis on reducing the environmental footprint of the built environment.
Aluminum veneer panel offers a combination of durability, design flexibility, and sustainable advantages that make it increasingly relevant in modern construction. Paired with Color Coated Aluminum Coil, these panels support environmentally conscious practices while enhancing the visual and functional aspects of buildings. As sustainability continues to shape industry priorities, materials like aluminum veneer panel are likely to remain central to construction strategies that aim to balance efficiency, aesthetics, and resource conservation.

 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Português
Português русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى